NCERT Solutions for Class 12th: Ch 2 Principles of Management Business Studies II
Page No: 67
Exercises
Multiple Choice
1. Principles of management are NOT(a) Universal(b) Flexible(c) Absolute(d) Behavioural► (c) Absolute
2. How are principles of management formed?(a) In a laboratory(b) By experiences of managers(c) By experiences of customers(d) By propagation of social scientists► (b) By experiences of managers
3. The principles of management are significant because of(a) Increase in efficiency(b) Initiative(c) Optimum utilisation of resources(d) Adaptation to changing technology► (c) Optimum utilisation of resources
4. Henri Fayol was a(a) Social Scientist(b) Mining Engineer(c) Accountant(d) Production engineer► (b) Mining Engineer
5. Which of the following statement best describes the principle of 'Division of Work'(a) Work should be divided into small tasks(b) Labour should be divided(c) Resources should be divided among jobs(d) It leads to specialisation► (a) Work should be divided into small tasks
6. ‘She/he keeps machines, materials, tools etc., ready for operations by concerned workers’. Whose work is described by this sentence under functional foremanship(a) Instruction Card Clerk(b) Repair Boss(c) Gang Boss(d) Route Clerk► (c) Gang Boss
7. Which of the following is NOT a Principle of management given by Taylor ?(a) Science, not rule of the Thumb(b) Functional foremanship(c) Maximum not restricted output(d) Harmony not discord► (b) Functional foremanship
Page No: 68
8. Management should find ‘One best way’ to perform a task. Which technique of Scientific management is defined in this sentence?(a) Time Study(b) Motion Study
(c) Fatigue Study
(d) Method Study
► (d) Method Study
9. Which of the following statements best describes ‘Mental Revolution’?(a) It implies change of attitude.(b) The management and workers should not play the game of one upmanship.(c) Both management and workers require each other.(d) Workers should be paid more wages.► (a) It implies change of attitude.
10. Which of the following statements is FALSE about Taylor and Fayol?
(a) Fayol was a mining engineer whereas Taylor was a mechanical engineer
(b) Fayol’s principles are applicable in specialised situations whereas Taylor’s principles have universal application
(c) Fayol’s principles were formed through personal experience whereas Taylor’s principles were formed through experimentation
(d) Fayol’s principles are applicable at the top level of management whereas Taylor’s principles are applicable at the shop floor.
► (b) Fayol’s principles are applicable in specialised situations whereas Taylor’s principles have universal application
Short Answer Type
1. How is the Principle of ‘Unity of Command’ useful to management? Explain briefly.
Answer
According to the Principle of ‘Unity of Command’ there should be one and only one boss for every individual employee. If an employee gets orders from two superiors at the same time the principle of unity of command is violated. It is very useful for a management as it prevent confusion regarding
tasks to be done. For example: a sales person is asked to clinch a deal with a buyer and is allowed to give 10% discount by the marketing manager. On the other side, finance department tells her/him not to offer more than 5% discount. This violates the principle which leads to confusion.
2. Define scientific management. State any three of its principles.
Answer
Scientific management means knowing exactly what you want men to do and seeing that they do it in the best and cheapest way.
Three principles of scientific management are:
→ Science not Rule of Thumb
→ Harmony, Not Discord
→ Cooperation, Not Individualism
3. If an organisation does not provide the right place for physical and human resources in an organisation, which principle is violated? What are the consequences of it?
Answer
The principle of order is violated in the given case. As per the Principle of Order, there should be a place for everything and everything in its place. Thus, when this principle is violated then a lot of time will waste in locating different resources. This will lead to decreased productivity and efficiency.
4. Explain any four points regarding significance of Principles of Management.
Answer
The four points regarding significance of Principles of Management are:
→ Providing managers with useful insights into reality: The principles of management provide the managers with useful insights into real world situations. These principles will add to their knowledge, ability and understanding of managerial situations and circumstances. It will also enable managers
to learn from past mistakes and conserve time by solving recurring problems quickly.
→ Optimum utilisation of resources and effective administration: Resources both human and
material available with the company are limited. Principles equip the managers to foresee the cause and effect relationships of their decisions and actions. Thus, the wastages associated with a trial-and-error approach can be overcome.
→ Scientific decisions: Decisions must be based on facts, thoughtful and justifiable in terms of the intended purposes. Management principles help in thoughtful decision-making. They emphasise logic rather than blind faith.
→ Meeting changing enviornment requirements: Management principles are flexible to adapt to dynamic business environment. For example, management principles emphasise division of work and
specialisation. In modern times this principle has been extended to the entire business whereby companies are specialising in their core competency and divesting non-core businesses.
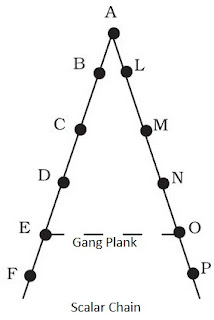
5. Explain the principle of ‘Scalar Chain’ and gang plank.
Answer
An organisation consists of superiors and subordinates. The formal lines of authority from highest to lowest ranks are known as scalar chain. For example: Let us consider a situation where there is one head ‘A’ who has two lines of authority under her or him. One line consists of B-C- D-E-F. Another line of authority under ‘A’ is L-M-N-O-P. If ‘E’ has to communicate with ‘O’ who is at the same level of authority then she/he has to traverse the route E-D-C-B-A-L-M-N-O. This is due to the principle of scalar chain
However, if there is an emergency then ‘E’ can directly contact ‘O’ through ‘Gang Plank'. This is a shorter route and has been provided so that communication is not delayed.
Long Answer Type
1. Explain the Principles of Scientific management given by Taylor.
Answer
The Principles of Scientific management given by Taylor are:
→ Science not Rule of Thumb: Taylor introduce method of scientific inquiry into the domain of management practice. He believed that there was only one best method to maximise efficiency. This method can be developed through study and analysis. The method so developed should substitute ‘Rule of Thumb’ throughout the organisation. Scientific method involved investigation of traditional methods through work-study, unifying the best practices and developing a standard method, which would be followed throughout the organisation.
→ Harmony, Not Discord: According to the Taylor if manager asked there worker to “get work done” it should not be difficult for them to appreciate their performance. He emphasised that there should be complete harmony between the management and workers. Both should realise that each one is important. Management should share the gains of the company, if any, with the workers. At the same time workers should work hard and willing to embrace for the good of the company.
→ Cooperation, Not Individualism: There should be complete cooperation between the labour and the management instead of individualism. Competition should be replaced by cooperation. Management should not close its ears to any constructive suggestions made by the employees. They should be rewarded for their suggestions which results in substantial reduction in costs. They should be part of management and, if any important decisions are taken, workers should be taken into confidence. At the same time workers should desist from going on strike and making unreasonable demands on the management. According to the Taylor there should be almost equal division of work and responsibility between worker and management.
→ Development of Each and Every Person to His or Her Greatest Efficiency and Prosperity: To maximize production all possible efforts are made to increase the efficiency of workers. Each person
should be scientifically selected. Then work assigned should suit her or his physical, mental and intellectual capabilities. To increase efficiency, they should be given the required training. Efficient employees would produce more and earn more. This will ensure their greatest efficiency and prosperity for both company and workers.
Page No: 69
2. Explain the following Principles of management given by Fayol with examples:
(a) Unity of direction
(b) Equity(c) Espirit de corps(d) Order(e) Centralisation and decentralisation(f) Initiative
Answer
(a) Unity of direction: All the units of an organisation should be moving towards the same objectives through coordinated and focused efforts. Each group of activities having the same objective must have one head and one plan. This ensures unity of action and coordination. For example, if a company is manufacturing motorcycles as well as cars then it should have two separate divisions for both of them with their respective heads and plans.
(b) Equity: This principle emphasises kindliness and justice in the behaviour of managers towards workers. This will ensure loyalty and devotion. Each employee is equal in the eyes of the management. There should be no discrimination against anyone on account of sex, religion, language, caste, belief or nationality etc.
(c) Espirit de corps: According to Fayol, Management should promote a team spirit of unity and harmony among employees. Management should promote teamwork especially in large organisations because otherwise objectives would be difficult to achieve. A manager should foster team spirit which will give rise to a spirit of mutual trust and belongingness among team members.
(d) Order: According to Fayol, People and materials must be in suitable places at appropriate time for maximum efficiency. If there is a fixed place for everything and it is present there, then there will be no hindrance in the activities of business or factory. This will lead to increased productivity and efficiency.
(e) Centralisation and decentralisation: Centralisation refers the concentration of decision-making authority is called centralisation whereas its dispersal among more than one person is known as decentralisation. In Fayol's view there is a need to balance subordinate involvement through decentralisation with managers’ retention of final authority through centralisation. The top management must keep the authority to take important decisions of the organization but adequate authority must be given to the lower level employees to take the department level decisions.
(f) Initiative: Workers should be encouraged to develop and carry out their plans for improvements according to Fayol. Initiative should be encouraged but it does not mean going against the established practices of the company for the sake of being different. A good company should have an employee suggestion system whereby initiative/ suggestions which result in substantial cost or time reduction should be rewarded.
3. Explain the technique of ‘Functional Foremanship’ and the concept of ‘Mental Revolution’ as enunciated by Taylor.
Answer
In the factory system, the foreman represents the managerial figure with whom the workers are in face-to-face contact on a daily basis. Foreman is the lowest ranking manager and the highest ranking worker who is pivot around whom revolves the entire production planning, implementation and control. Thus, Taylor concentrated on improving the performance of this role in the factory set-up. In fact, he identified a list of qualities of a good foreman and found that no single person could fit them all. Thus, he suggested there should be eight persons through which the functions of a foreman should be accomplished. This technique was given the name Functional Foremanship.
According to this, planning and execution functions should be separated. Under the factory manager there would be a planning incharge and a production incharge. Each incharge would have four personnel under him or her.
The following are the four persons that worked under the planning incharge.
• Instruction Card Clerk- To give instructions to the workers.
• Route Clerk- To show the route of production.
• Time and Cost Clerk- To take care about the time and costs.
• Disciplinarian- To ensure that discipline is being maintained.
The following are the four persons that worked under the production incharge.
• Speed Boss- To ensure timely completion of tasks
• Gang Boss- To keep the machines and tools ready for the workers.
• Repair Boss- To ensure proper working of the machines.
• Inspector- To control the quality of work done.
Mental revolution involves a change in the attitude of workers and management towards one another from competition to cooperation. Both should realise that they require one another. Both should aim to increase the size of surplus. This would eliminate the need for any agitation. Management should share a part of surplus with workers. Workers should also contribute their might so that the company makes profits. This attitude will be good for both of them and also for the company.
4. Discuss the following techniques of Scientific Work Study:
(a) Time Study
(b) Motion Study
(c) Fatigue Study
(d) Method Study
(e) Simplification and standardisation of work
Answer
(a) Time Study: It determines the standard time taken to perform a well-defined job. The standard time is fixed for the whole of the task by taking several readings. The method of time study will depend upon volume and frequency of the task, the cycle time of the operation and time measurement costs. The objective of time study is to determine the number of workers to be employed, frame suitable incentive schemes and determine labour costs. For example, if, on the basis of observations it is determined that one person can finish making 1 cardboard box in 20 minutes then, in a working day of 8 hours in a shift and deducting one hour for rest and lunch each worker should make 21 cardboard box.
(b) Motion Study: The study refers to the study of movements like lifting, putting objects, sitting and changing positions etc., which are undertaken while doing a typical job. Unnecessary movements are sought to be eliminated so that it takes less time to complete the job efficiently. For example, Taylor and his associate Frank Gailberth were able to reduce motions in brick layering from 18 to just 5.
(c) Fatigue Study: This study determine the amount and frequency of rest intervals in completing a task. If a worker works continuously physical and mental fatigue sets. The rest intervals will help one to regain stamina and work again with the same capacity. This will result in increased productivity. For example, normally in a plant, work takes place in three shifts of eight hours each.
(d) Method Study: The objective of method study is to find out one best way of doing the job. To determine the best way there are several parameters. Right from procurement of raw materials till the final product is delivered to the customer every activity is part of method study. The objective of the whole exercise is to minimise the cost of production and maximise the quality and satisfaction of the customer. For this purpose many techniques like process charts and operations research etc are used.
(e) Simplification and standardisation of work: Standardisation refers to the process of setting standards for every business activity such as standardisation of process, raw material, time, product, machinery, methods or working conditions. These standards are the benchmarks, which must be adhered to during production. Other techniques by Taylor, such as method study, fatigue study and time study are also based on the concept of standardisation.
Simplification aims at eliminating unnecessary diversity of products. It results in savings of cost of
labour, machines and tools. It implies reduced inventories, fuller utilisation of equipment and increasing turnover.
5. Discuss the differences between the contributions of Taylor and Fayol.
Answer
| Basis of Difference | Contributions of Henri Fayol | Contributions of F.W. Taylor |
| Perspective | Main concentration on Top level of
management | Main concentration on Shop floor level of a factory |
| Unity of Command | He was Staunch Proponent | He did not feel that it is important as under functional foremanship a worker received orders from eight specialists |
| Applicability | Principles are accepted everywhere and are universal in nature. | Principles are applicable to specialized situations. |
| Basis of formation | Theories are based on Personal experience | Theories are based on Observations and experimentation |
| Focus | The main focus was on improving overall
administration | The main focus was on increasing Productivity |
| Personality | Fayol was a mining engineer or practitioner. | Taylor was a mechanical engineer or scientist. |
| Expression | General Theory of Administration | Scientific Management |
6. Discuss the relevance of Taylor and Fayol's contribution in the contemporary business environment.
Answer
The principles of Taylor and Fayol play an important role in contemporary business environment. Taylor's scientific management principles and Fayol's administrative principles have contributed
immensely to the knowledge of management, which has formed a basis for further practice by managers. Their contributions are complementary to each other. Although with the change
of environment in which business is done, the interpretation of these but they prove as important guidelines in complex real business situations. Managers can use them in different situations to solve the recurring problems. Decisions taken on the basis of these principles are based on facts and logic making more appropriate. As they are developed over time by a continuous process of observations and experimentation therefore they provide useful insight into the real business situations. The principles have universal applicability. These principles mainly aim at increasing the efficiency in the organisation along with optimum utilisation of resources. Also, these focus on mutual co-operation between employers and employees while maintaining a harmonious work environment.