NCERT Solutions for Class 9th: Ch 2 Polynomials Maths (Part -2)
Page No: 43Exercise 2.4
1. Determine which of the following polynomials has (x + 1) a factor:
(i) x3 + x2 + x + 1
(ii) x4 + x3 + x2 + x + 1
(iii) x4 + 3x3 + 3x2 + x + 1
(iii) x4 + 3x3 + 3x2 + x + 1
(iv) x3 - x2 - (2 + √2)x + √2
Answer
(i) If (x + 1) is a factor of p(x) = x3 + x2 + x + 1, p(-1) must be zero.
Here, p(x) = x3 + x2 + x + 1
p(-1) = (-1)3 + (-1)2 + (-1) + 1
= -1 + 1 - 1 + 1 = 0
Therefore, x + 1 is a factor of this polynomial
(ii) If (x + 1) is a factor of p(x) = x4 + x3 + x2 + x + 1, p(-1) must be zero.
Here, p(x) = x4 + x3 + x2 + x + 1
p(-1) = (-1)4 + (-1)3 + (-1)2 + (-1) + 1
= 1 - 1 + 1 - 1 + 1 = 1
As, p(-1) ≠ 0Answer
(i) If (x + 1) is a factor of p(x) = x3 + x2 + x + 1, p(-1) must be zero.
Here, p(x) = x3 + x2 + x + 1
p(-1) = (-1)3 + (-1)2 + (-1) + 1
= -1 + 1 - 1 + 1 = 0
Therefore, x + 1 is a factor of this polynomial
(ii) If (x + 1) is a factor of p(x) = x4 + x3 + x2 + x + 1, p(-1) must be zero.
Here, p(x) = x4 + x3 + x2 + x + 1
p(-1) = (-1)4 + (-1)3 + (-1)2 + (-1) + 1
= 1 - 1 + 1 - 1 + 1 = 1
Therefore, x + 1 is not a factor of this polynomial
(iii)If (x + 1) is a factor of polynomial p(x) = x4 + 3x3 + 3x2 + x + 1, p(- 1) must be 0.
p(-1) = (-1)4 + 3(-1)3 + 3(-1)2 + (-1) + 1
= 1 - 3 + 3 - 1 + 1 = 1
As, p(-1) ≠ 0
Therefore, x + 1 is not a factor of this polynomial.
p(x) = x3 - x2 - (2 + √2)x + √2, p(- 1) must be 0.
p(-1) = (-1)3 - (-1)2 - (2 + √2) (-1) + √2= -1 - 1 + 2 + √2 + √2
=2√2
As, p(-1) ≠ 0
Therefore,, x + 1 is not a factor of this polynomial.
2. Use the Factor Theorem to determine whether g(x) is a factor of p(x) in each of the following cases:
(i) p(x) = 2x3 + x2 - 2x - 1, g(x) = x + 1
(ii) p(x) = x3 + 3x2 + 3x + 1, g(x) = x + 2
(iii) p(x) = x3 - 4 x2 + x + 6, g(x) = x - 3
Answer
(i) If g(x) = x + 1 is a factor of given polynomial p(x), p(- 1) must be zero.
p(x) = 2x3 + x2 - 2x - 1
p(- 1) = 2(-1)3 + (-1)2 - 2(-1) - 1
= 2(- 1) + 1 + 2 - 1 = 0
Hence, g(x) = x + 1 is a factor of given polynomial.
(ii) If g(x) = x + 2 is a factor of given polynomial p(x), p(- 2) must be 0.
p(x) = x3 +3x2 + 3x + 1
p(-2) = (-2)3 + 3(- 2)2 + 3(- 2) + 1
= -8 + 12 - 6 + 1
= -1
As, p(-2) ≠ 0
Hence g(x) = x + 2 is not a factor of given polynomial.
(iii) If g(x) = x - 3 is a factor of given polynomial p(x), p(3) must be 0.
p(x) = x3 - 4x2 + x + 6
p(3) = (3)3 - 4(3)2 + 3 + 6
= 27 - 36 + 9 = 0
Therefore,, g(x) = x - 3 is a factor of given polynomial.
Page No: 44
3. Find the value of k, if x - 1 is a factor of p(x) in each of the following cases:(i) p(x) = x2 + x + k
(ii) p(x) = 2x2 + kx + √2
(iii) p(x) = kx2 - √2x + 1
(iv) p(x) = kx2 - 3x + k
Answer
(i) If x - 1 is a factor of polynomial p(x) = x2 + x + k, then
p(1) = 0
⇒ (1)2 + 1 + k = 0
⇒ 2 + k = 0
⇒ k = - 2
⇒ (1)2 + 1 + k = 0
⇒ 2 + k = 0
⇒ k = - 2
Therefore, value of k is -2.
(ii) If x - 1 is a factor of polynomial p(x) = 2x2 + kx + √2, then
p(1) = 0
⇒ 2(1)2 + k(1) + √2 = 0
⇒ 2 + k + √2 = 0
⇒ k = -2 - √2 = -(2 + √2)
Therefore, value of k is -(2 + √2).
(iii) If x - 1 is a factor of polynomial p(x) = kx2 - √2x + 1, then
p(1) = 0
⇒ k(1)2 - √2(1) + 1 = 0
⇒ k - √2 + 1 = 0
⇒ k = √2 - 1
Therefore, value of k is √2 - 1.
(iv) If x - 1 is a factor of polynomial p(x) = kx2 - 3x + k, then
p(1) = 0
⇒ k(1)2 + 3(1) + k = 0
⇒ k - 3 + k = 0
⇒ 2k - 3 = 0
⇒ k = 3/2
Therefore, value of k is 3/2.
4. Factorise:
(i) 12x2 + 7x + 1
(ii) 2x2 + 7x + 3
(iii) 6x2 + 5x - 6
(iv) 3x2 - x - 4
Answer
(i) 12x2 + 7x + 1
= 12x2 - 4x - 3x+ 1
= 4x (3x - 1) - 1 (3x - 1)
= (3x - 1) (4x - 1)
(ii) 2x2 + 7x + 3
= 2x2 + 6x + x + 3
= 2x (x + 3) + 1 (x + 3)
= (x + 3) (2x + 1)
(iii) 6x2 + 5x - 6
= 6x2 + 9x - 4x - 6
= 3x (2x + 3) - 2 (2x + 3)
= (2x + 3) (3x - 2)
= (2x + 3) (3x - 2)
(iv) 3x2 - x - 4
= 3x2 - 4x + 3x - 4
= x (3x - 4) + 1 (3x - 4)
= (3x - 4) (x + 1)
5. Factorise:
(i) x3 - 2x2 - x + 2
(ii) x3 - 3x2 - 9x - 5
(iii) x3 + 13x2 + 32x + 20
(iii) x3 + 13x2 + 32x + 20
(iv) 2y3 + y2 - 2y - 1
Answer
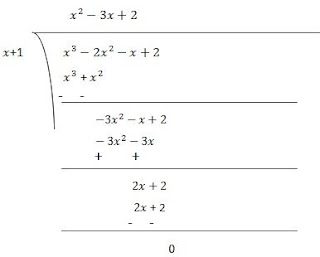
(i) Let p(x) = x3 - 2x2 - x + 2
Factors of 2 are ±1 and ± 2
By trial method, we find that
p(1) = 0
So, (x+1) is factor of p(x)
Now,
p(x) = x3 - 2x2 - x + 2
p(-1) = (-1)3 - 2(-1)2 - (-1) + 2 = -1 -2 + 1 + 2 = 0
Therefore, (x+1) is the factor of p(x)
Answer
(i) Let p(x) = x3 - 2x2 - x + 2
Factors of 2 are ±1 and ± 2
By trial method, we find that
p(1) = 0
So, (x+1) is factor of p(x)
Now,
p(x) = x3 - 2x2 - x + 2
p(-1) = (-1)3 - 2(-1)2 - (-1) + 2 = -1 -2 + 1 + 2 = 0
Therefore, (x+1) is the factor of p(x)

Now, Dividend = Divisor × Quotient + Remainder
(x+1) (x2 - 3x + 2)= (x+1) (x2 - x - 2x + 2)
= (x+1) {x(x-1) -2(x-1)}
= (x+1) (x-1) (x+2)
(ii) Let p(x) = x3 - 3x2 - 9x - 5
Factors of 5 are ±1 and ±5
By trial method, we find that
p(5) = 0
So, (x-5) is factor of p(x)
Now,
p(x) = x3 - 2x2 - x + 2
p(5) = (5)3 - 3(5)2 - 9(5) - 5 = 125 - 75 - 45 - 5 = 0
Therefore, (x-5) is the factor of p(x)
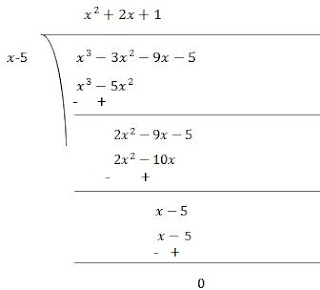
Now, Dividend = Divisor × Quotient + Remainder
(x-5) (x2 + 2x + 1)= (x-5) (x2 + x + x + 1)
= (x-5) {x(x+1) +1(x+1)}
= (x-5) (x+1) (x+1)
(iii) Let p(x) = x3 + 13x2 + 32x + 20
Factors of 20 are ±1, ±2, ±4, ±5, ±10 and ±20
By trial method, we find that
p(-1) = 0
So, (x+1) is factor of p(x)
Now,
p(x) = x3 + 13x2 + 32x + 20
p(-1) = (-1)3 + 13(-1)2 + 32(-1) + 20 = -1 + 13 - 32 + 20 = 0
Therefore, (x+1) is the factor of p(x)

(iv) Let p(y) = 2y3 + y2 - 2y - 1
Factors of ab = 2× (-1) = -2 are ±1 and ±2
By trial method, we find that
p(1) = 0
So, (y-1) is factor of p(y)
Now,
p(y) = 2y3 + y2 - 2y - 1
p(1) = 2(1)3 + (1)2 - 2(1) - 1 = 2 +1 - 2 - 1 = 0
Therefore, (y-1) is the factor of p(y)
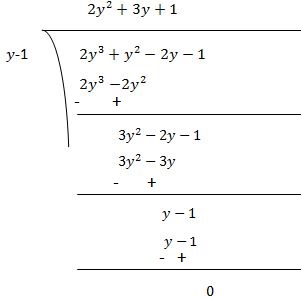
Page No: 48
Exercise 2.5
1. Use suitable identities to find the following products:
(i) (x + 4) (x + 10) (ii) (x + 8) (x – 10) (iii) (3x + 4) (3x – 5)
(iv) (y2 + 3/2) (y2 - 3/2) (v) (3 - 2x) (3 + 2x)
Answer
(i) Using identity, (x + a) (x + b) = x2 + (a + b) x + ab
In (x + 4) (x + 10), a = 4 and b = 10
Now,
(x + 4) (x + 10) = x2 + (4 + 10)x + (4 × 10)
= x2 + 14x + 40
(ii) (x + 8) (x – 10)
Using identity, (x + a) (x + b) = x2 + (a + b) x + ab
Here, a = 8 and b = –10
(x + 8) (x – 10) = x2 + {8 +(– 10)}x + {8×(– 10)}
= x2 + (8 – 10)x – 80
= x2 – 2x – 80
(iii) (3x + 4) (3x – 5)
Using identity, (x + a) (x + b) = x2 + (a + b) x + ab
Here, x = 3x , a = 4 and b = -5
(3x + 4) (3x – 5) = (3x) 2 + {4 + (-5)}3x + {4×(-5)}
= 9x2 + 3x(4 - 5) - 20
= 9x2 - 3x - 20
(iv) (y2 + 3/2) (y2 - 3/2)
Using identity, (x + y) (x -y) = x2 - y2
Here, x = y2 and y = 3/2
(y2 + 3/2) (y2 - 3/2) = (y2)2 - (3/2)2
= y4 - 9/4
(v) (3 - 2x) (3 + 2x)
Using identity, (x + y) (x -y) = x2 - y2
Here, x = 3 and y = 2x
(3 - 2x) (3 + 2x) = 32 - (2x)2
= 9 - 4x2
2. Evaluate the following products without multiplying directly:
(i) 103 × 107 (ii) 95 × 96 (iii) 104 × 96
Answer
(i) 103 × 107 = (100 + 3) (100 + 7)
Using identity, (x + a) (x + b) = x2 + (a + b) x + ab
(iii) Let p(x) = x3 + 13x2 + 32x + 20
Factors of 20 are ±1, ±2, ±4, ±5, ±10 and ±20
By trial method, we find that
p(-1) = 0
So, (x+1) is factor of p(x)
Now,
p(x) = x3 + 13x2 + 32x + 20
p(-1) = (-1)3 + 13(-1)2 + 32(-1) + 20 = -1 + 13 - 32 + 20 = 0
Therefore, (x+1) is the factor of p(x)

Now, Dividend = Divisor × Quotient + Remainder
(x+1) (x2 + 12x + 20)= (x+1) (x2 + 2x + 10x + 20)
= (x-5) {x(x+2) +10(x+2)}
= (x-5) (x+2) (x+10)(iv) Let p(y) = 2y3 + y2 - 2y - 1
Factors of ab = 2× (-1) = -2 are ±1 and ±2
By trial method, we find that
p(1) = 0
So, (y-1) is factor of p(y)
Now,
p(y) = 2y3 + y2 - 2y - 1
p(1) = 2(1)3 + (1)2 - 2(1) - 1 = 2 +1 - 2 - 1 = 0
Therefore, (y-1) is the factor of p(y)
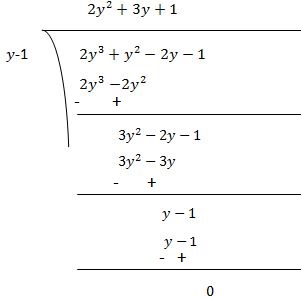
Now, Dividend = Divisor × Quotient + Remainder
(y-1) (2y2 + 3y + 1)= (y-1) (2y2 + 2y + y + 1)
= (y-1) {2y(y+1) +1(y+1)}
= (y-1) (2y+1) (y+1)Page No: 48
Exercise 2.5
1. Use suitable identities to find the following products:
(i) (x + 4) (x + 10) (ii) (x + 8) (x – 10) (iii) (3x + 4) (3x – 5)
(iv) (y2 + 3/2) (y2 - 3/2) (v) (3 - 2x) (3 + 2x)
Answer
(i) Using identity, (x + a) (x + b) = x2 + (a + b) x + ab
In (x + 4) (x + 10), a = 4 and b = 10
Now,
(x + 4) (x + 10) = x2 + (4 + 10)x + (4 × 10)
= x2 + 14x + 40
(ii) (x + 8) (x – 10)
Using identity, (x + a) (x + b) = x2 + (a + b) x + ab
Here, a = 8 and b = –10
(x + 8) (x – 10) = x2 + {8 +(– 10)}x + {8×(– 10)}
= x2 + (8 – 10)x – 80
= x2 – 2x – 80
(iii) (3x + 4) (3x – 5)
Using identity, (x + a) (x + b) = x2 + (a + b) x + ab
Here, x = 3x , a = 4 and b = -5
(3x + 4) (3x – 5) = (3x) 2 + {4 + (-5)}3x + {4×(-5)}
= 9x2 + 3x(4 - 5) - 20
= 9x2 - 3x - 20
(iv) (y2 + 3/2) (y2 - 3/2)
Using identity, (x + y) (x -y) = x2 - y2
Here, x = y2 and y = 3/2
(y2 + 3/2) (y2 - 3/2) = (y2)2 - (3/2)2
= y4 - 9/4
(v) (3 - 2x) (3 + 2x)
Using identity, (x + y) (x -y) = x2 - y2
Here, x = 3 and y = 2x
(3 - 2x) (3 + 2x) = 32 - (2x)2
= 9 - 4x2
2. Evaluate the following products without multiplying directly:
(i) 103 × 107 (ii) 95 × 96 (iii) 104 × 96
Answer
(i) 103 × 107 = (100 + 3) (100 + 7)
Using identity, (x + a) (x + b) = x2 + (a + b) x + ab
Here, x = 100, a = 3 and b = 7
103 × 107 = (100 + 3) (100 + 7) = (100)2 + (3 + 7)10 + (3 × 7)
= 10000 + 100 + 21
= 11021
(ii) 95 × 96 = (90 + 5) (90 + 4)
Using identity, (x + a) (x + b) = x2 + (a + b) x + ab
Here, x = 90, a = 5 and b = 4
95 × 96 = (90 + 5) (90 + 4) = 902 + 90(5 + 6) + (5 × 6)
= 8100 + (11 × 90) + 30
= 8100 + 990 + 30 = 9120
103 × 107 = (100 + 3) (100 + 7) = (100)2 + (3 + 7)10 + (3 × 7)
= 10000 + 100 + 21
= 11021
(ii) 95 × 96 = (90 + 5) (90 + 4)
Using identity, (x + a) (x + b) = x2 + (a + b) x + ab
Here, x = 90, a = 5 and b = 4
95 × 96 = (90 + 5) (90 + 4) = 902 + 90(5 + 6) + (5 × 6)
= 8100 + (11 × 90) + 30
= 8100 + 990 + 30 = 9120
(iii) 104 × 96 = (100 + 4) (100 - 4)
Using identity, (x + y) (x -y) = x2 - y2
Here, x = 100 and y = 4
104 × 96 = (100 + 4) (100 - 4) = (100)2 - (4)2 = 10000 - 16 = 9984
3. Factorise the following using appropriate identities:
(i) 9x2 + 6xy + y2 (ii) 4y2 - 4y + 1 (iii) x2 - y2/100
Answer
(i) 9x2 + 6xy + y2 = (3x) 2 + (2×3x×y) + y2
Using identity, (a + b)2 = a2 + 2ab + b2
Here, a = 3x and b = y
9x2 + 6xy + y2 = (3x) 2 + (2×3x×y) + y2 = (3x + y)2 = (3x + y) (3x + y)
(ii) 4y2 - 4y + 1 = (2y)2 - (2×2y×1) + 12
Using identity, (a - b)2 = a2 - 2ab + b2
Here, a = 2y and b = 1
4y2 - 4y + 1 = (2y)2 - (2×2y×1) + 12 = (2y - 1)2 = (2y - 1) (2y - 1)
(iii) x2 - y2/100 = x2 - (y/10)2
Using identity, a2 - b2 = (a + b) (a - b)
Here, a = x and b = (y/10)
x2 - y2/100 = x2 - (y/10)2 = (x - y/10) (x + y/10)
Page No: 49
4. Expand each of the following, using suitable identities:
(i) (x + 2y + 4z)2 (ii) (2x – y + z)2 (iii) (–2x + 3y + 2z)2
(iv) (3a – 7b – c)2 (v) (–2x + 5y – 3z)2 (vi) [1/4 a - 1/2 b + 1]2
Answer
(i) (x + 2y + 4z)2
Using identity, (a + b + c)2 = a2 + b2 + c2 + 2ab + 2bc + 2ca
Here, a = x, b = 2y and c = 4z
(x + 2y + 4z)2 = x2 + (2y)2 + (4z)2 + (2×x×2y) + (2×2y×4z) + (2×4z×x)
= x2 + 4y2 + 16z2 + 4xy + 16yz + 8xz
(ii) (2x – y + z)2
Using identity, (a + b + c)2 = a2 + b2 + c2 + 2ab + 2bc + 2ca
Here, a = 2x, b = -y and c = z
(2x – y + z)2 = (2x)2 + (-y)2 + z2 + (2×2x×-y) + (2×-y×z) + (2×z×2x)
= 4x2 + y2 + z2 - 4xy - 2yz + 4xz
(iii) (–2x + 3y + 2z)2
Using identity, (a + b + c)2 = a2 + b2 + c2 + 2ab + 2bc + 2ca
Here, a = -2x, b = 3y and c = 2z
(–2x + 3y + 2z)2 = (-2x)2 + (3y)2 + (2z)2 + (2×-2x×3y) + (2×3y×2z) + (2×2z×-2x)
= 4x2 + 9y2 + 4z2 - 12xy + 12yz - 8xz
(iv) (3a – 7b – c)2
Using identity, (a + b + c)2 = a2 + b2 + c2 + 2ab + 2bc + 2ca
Here, a = 3a, b = -7b and c = -c
(3a – 7b – c)2 = (3a)2 + (-7b)2 + (-c)2 + (2×3a×-7b) + (2×-7b×-c) + (2×-c×3a)
= 9a2 + 49b2 + c2 - 42ab + 14bc - 6ac
(v) (–2x + 5y – 3z)2
Using identity, (a + b + c)2 = a2 + b2 + c2 + 2ab + 2bc + 2ca
Here, a = -2x, b = 5y and c = -3z
(–2x + 5y – 3z)2 = (-2x)2 + (5y)2 + (-3z)2 + (2×-2x×5y) + (2×5y×-3z) + (2×-3z×-2x)
= 4x2 + 25y2 + 9z2 - 20xy - 30yz + 12xz
(vi) [1/4 a - 1/2 b + 1]2
Using identity, (a + b + c)2 = a2 + b2 + c2 + 2ab + 2bc + 2ca
Here, a = 1/4 a, b = -1/2 b and c = 1
[1/4 a - 1/2 b + 1]2 = (1/4 a)2 + (-1/2 b)2 + 12 + (2×1/4 a×-1/2 b) + (2×-1/2 b×1) + (2×1×1/4 a)
= 1/16 a2 + 1/4 b2 + 1 - 1/4 ab - b + 1/2 a
5. Factorise:
(i) 4x2 + 9y2 + 16z2 + 12xy - 24yz - 16xz
(ii) 2x2 + y2 + 8z2 - 2√2 xy + 4√2 yz - 8xz
Answer
(i) 4x2 + 9y2 + 16z2 + 12xy - 24yz - 16xz
Using identity, (a + b + c)2 = a2 + b2 + c2 + 2ab + 2bc + 2ca
4x2 + 9y2 + 16z2 + 12xy - 24yz - 16xz
= (2x)2 + (3y)2 + (-4z)2 + (2×2x×3y) + (2×3y×-4z) + (2×-4z×2x)
= (2x + 3y - 4z)2
= (2x + 3y - 4z) (2x + 3y - 4z)
(ii) 2x2 + y2 + 8z2 - 2√2 xy + 4√2 yz - 8xz
Using identity, (a + b + c)2 = a2 + b2 + c2 + 2ab + 2bc + 2ca
2x2 + y2 + 8z2 - 2√2 xy + 4√2 yz - 8xz
= (-√2x)2 + (y)2 + (2√2z)2 + (2×-√2x×y) + (2×y×2√2z) + (2×2√2z×-√2x)
= (-√2x + y + 2√2z)2
= (-√2x + y + 2√2z) (-√2x + y + 2√2z)
6. Write the following cubes in expanded form:
(i) (2x + 1)3 (ii) (2a – 3b)3 (iii) [3/2 x + 1]3 (iv) [x - 2/3 y]3
Answer
(i) (2x + 1)3
Using identity, (a + b)3 = a3 + b3 + 3ab(a + b)
(2x + 1)3 = (2x)3 + 13 + (3×2x×1)(2x + 1)
= 8x3 + 1 + 6x(2x + 1)
= 8x3 + 12x2 + 6x + 1
(ii) (2a – 3b)3
Using identity, (a - b)3 = a3 - b3 - 3ab(a - b)
(2a – 3b)3 = (2a)3 - (3b)3 - (3×2a×3b)(2a - 3b)
= 8a3 - 27b3 - 18ab(2a - 3b)
= 8a3 - 27b3 - 36a2b + 54ab2
(iii) [3/2 x + 1]3
Using identity, (a + b)3 = a3 + b3 + 3ab(a + b)
[3/2 x + 1]3 = (3/2 x)3 + 13 + (3×3/2 x×1)(3/2 x + 1)
= 27/8 x3 + 1 + 9/2 x(3/2 x + 1)
= 27/8 x3 + 1 + 27/4 x2 + 9/2 x
= 27/8 x3 + 27/4 x2 + 9/2 x + 1
(iv) [x - 2/3 y]3
Using identity, (a - b)3 = a3 - b3 - 3ab(a - b)
[x - 2/3 y]3 = (x)3 - (2/3 y)3 - (3×x×2/3 y)(x - 2/3 y)
= x3 - 8/27y3 - 2xy(x - 2/3 y)
= x3 - 8/27y3 - 2x2y + 4/3xy2
7. Evaluate the following using suitable identities:
(i) (99)3 (ii) (102)3 (iii) (998)3
Answer
(i) (99)3 = (100 - 1)3
Using identity, (a - b)3 = a3 - b3 - 3ab(a - b)
(100 - 1)3 = (100)3 - 13 - (3×100×1)(100 - 1)
= 1000000 - 1 - 300(100 - 1)
= 1000000 - 1 - 30000 + 300
= 970299
(ii) (102)3 = (100 + 2)3
Using identity, (a + b)3 = a3 + b3 + 3ab(a + b)
(100 + 2)3 = (100)3 + 23 + (3×100×2)(100 + 2)
= 1000000 + 8 + 600(100 + 2)
= 1000000 + 8 + 60000 + 1200
= 1061208
(iii) (998)3
Using identity, (a - b)3 = a3 - b3 - 3ab(a - b)
(1000 - 2)3 = (1000)3 - 23 - (3×1000×2)(1000 - 2)
= 100000000 - 8 - 6000(1000 - 2)
= 100000000 - 8- 600000 + 12000
= 994011992
8. Factorise each of the following:
(i) 8a3 + b3 + 12a2b + 6ab2 (ii) 8a3 - b3 - 12a2b + 6ab2
(iii) 27 - 125a3 - 135a + 225a2 (iv) 64a3 - 27b3 - 144a2b + 108ab2
(v) 27p3 - 1/216 - 9/2 p2 + 1/4 p
Answer
(i) 8a3 + b3 + 12a2b + 6ab2
Using identity, (a + b)3 = a3 + b3 + 3a2b + 3ab2
8a3 + b3 + 12a2b + 6ab2
= (2a)3 + b3 + 3(2a)2b + 3(2a)(b)2
= (2a + b)3
= (2a + b)(2a + b)(2a + b)
(ii) 8a3 - b3 - 12a2b + 6ab2
Using identity, (a - b)3 = a3 - b3 - 3a2b + 3ab2
8a3 - b3 - 12a2b + 6ab2= (2a)3 - b3 - 3(2a)2b + 3(2a)(b)2
= (2a - b)3
= (2a - b)(2a - b)(2a - b)
(iii) 27 - 125a3 - 135a + 225a2
Using identity, (a - b)3 = a3 - b3 - 3a2b + 3ab2
27 - 125a3 - 135a + 225a2= 33 - (5a)3 - 3(3)2(5a) + 3(3)(5a)2
= (3 - 5a)3
= (3 - 5a)(3 - 5a)(3 - 5a)
(iv) 64a3 - 27b3 - 144a2b + 108ab2
Using identity, (a - b)3 = a3 - b3 - 3a2b + 3ab2
64a3 - 27b3 - 144a2b + 108ab2= (4a)3 - (3b)3 - 3(4a)2(3b) + 3(4a)(3b)2
= (4a - 3b)3
= (4a - 3b)(4a - 3b)(4a - 3b)
(v) 27p3 - 1/216 - 9/2 p2 + 1/4 p
Using identity, (a - b)3 = a3 - b3 - 3a2b + 3ab2
27p3 - 1/216 - 9/2 p2 + 1/4 p
= (3p)3 - (1/6)3 - 3(3p)2(1/6) + 3(3p)(1/6)2
= (3p - 1/6)3
= (3p - 1/6)(3p - 1/6)(3p - 1/6)
9. Verify : (i) x3 + y3 = (x + y) (x2 - xy + y2) (ii) x3 - y3 = (x - y) (x2 + xy + y2)
Answer
(i) x3 + y3 = (x + y) (x2 - xy + y2)
We know that,
(x + y)3 = x3 + y3 + 3xy(x + y)
⇒ x3 + y3 = (x + y)3 - 3xy(x + y)
⇒ x3 + y3 = (x + y)[(x + y)2 - 3xy] {Taking (x+y) common}
⇒ x3 + y3 = (x + y)[(x2 + y2 + 2xy) - 3xy]
⇒ x3 + y3 = (x + y)(x2 + y2 - xy)
(ii) x3 - y3 = (x - y) (x2 + xy + y2 )
We know that,
(x - y)3 = x3 - y3 - 3xy(x - y)
⇒ x3 - y3 = (x - y)3 + 3xy(x - y)
⇒ x3 + y3 = (x - y)[(x - y)2 + 3xy] {Taking (x-y) common}
⇒ x3 + y3 = (x - y)[(x2 + y2 - 2xy) + 3xy]
⇒ x3 + y3 = (x + y)(x2 + y2 + xy)
10. Factorise each of the following:
(i) 27y3 + 125z3 (ii) 64m3 - 343n3
Answer
(i) 27y3 + 125z3
Using identity, x3 + y3 = (x + y) (x2 - xy + y2)
27y3 + 125z3 = (3y)3 + (5z)3
= (3y + 5z) {(3y)2 - (3y)(5z) + (5z)2}
= (3y + 5z) (9y2 - 15yz + 25z)2
(ii) 64m3 - 343n3
Using identity, x3 - y3 = (x - y) (x2 + xy + y2 )
64m3 - 343n3 = (4m)3 - (7n)3
= (4m + 7n) {(4m)2 + (4m)(7n) + (7n)2}
= (4m + 7n) (16m2 + 28mn + 49n)2
11. Factorise : 27x3 + y3 + z3 - 9xyz
Answer
27x3 + y3 + z3 - 9xyz = (3x)3 + y3 + z3 - 3×3xyz
Using identity, x3 + y3 + z3 - 3xyz = (x + y + z)(x2 + y2 + z2 - xy - yz - xz)
27x3 + y3 + z3 - 9xyz
= (3x + y + z) {(3x)2 + y2 + z2 - 3xy - yz - 3xz}
= (3x + y + z) (9x2 + y2 + z2 - 3xy - yz - 3xz)
12. Verify that: x3 + y3 + z3 - 3xyz = 1/2(x + y + z) [(x - y)2 + (y - z)2 +
Answer
We know that,
x3 + y3 + z3 - 3xyz = (x + y + z)(x2 + y2 + z2 - xy - yz - xz)
⇒ x3 + y3 + z3 - 3xyz = 1/2×(x + y + z) 2(x2 + y2 + z2 - xy - yz - xz)
= 1/2(x + y + z) (2x2 + 2y2 + 2z2 - 2xy - 2yz - 2xz)
= 1/2(x + y + z) [(x2 + y2 -2xy) + (y2 + z2 - 2yz) + (x2 + z2 - 2xz)]
= 1/2(x + y + z) [(x - y)2 + (y - z)2 + (z - x)2]
13. If x + y + z = 0, show that x3 + y3 + z3 = 3xyz.
Answer
We know that,
x3 + y3 + z3 - 3xyz = (x + y + z)(x2 + y2 + z2 - xy - yz - xz)
Now put (x + y + z) = 0,
x3 + y3 + z3 - 3xyz = (0)(x2 + y2 + z2 - xy - yz - xz)
⇒ x3 + y3 + z3 - 3xyz = 0
14. Without actually calculating the cubes, find the value of each of the following:
(i) (-12)3 + (7)3 + (5)3
(ii) (28)3 + (–15)3 + (-13)3
Answer
(i) (-12)3 + (7)3 + (5)3
Let x = -12, y = 7 and z = 5
We observed that, x + y + z = -12 + 7 + 5 = 0
We know that if,
x + y + z = 0, then x3 + y3 + z3 = 3xyz
(-12)3 + (7)3 + (5)3 = 3(-12)(7)(5) = -1260
(ii) (28)3 + (–15)3 + (-13)3
Let x = 28, y = -15 and z = -13
We observed that, x + y + z = 28 - 15 - 13 = 0
We know that if,
x + y + z = 0, then x3 + y3 + z3 = 3xyz
(28)3 + (–15)3 + (-13)3 = 3(28)(-15)(-13) = 16380
15. Give possible expressions for the length and breadth of each of the following rectangles, in which their areas are given:
(i) Area : 25a2 - 35a + 12
(ii) Area : 35 y2 + 13y - 12
Answer
(i) Area : 25a2 - 35a + 12
Since, area is product of length and breadth therefore by factorizing the given area, we can know the length and breadth of rectangle.
25a2 - 35a + 12
= 25a2 - 15a -20a + 12
= 5a(5a - 3) - 4(5a - 3)
= (5a - 4)(5a - 3)
Possible expression for length = 5a - 4
Possible expression for breadth = 5a - 3
(ii) Area : 35 y2 + 13y - 12
35 y2 + 13y - 12
= 35y2 - 15y + 28y - 12
= 5y(7y - 3) + 4(7y - 3)
= (5y + 4)(7y - 3)
Possible expression for length = (5y + 4)
Possible expression for breadth = (7y - 3)
Page No: 50
16. What are the possible expressions for the dimensions of the cuboids whose volumes are given below? (i) Volume : 3x2 - 12x
(ii) Volume : 12ky2 + 8ky - 20k
Answer
(i) Volume : 3x2 - 12x
Since, volume is product of length, breadth and height therefore by factorizing the given volume, we can know the length, breadth and height of the cuboid.
3x2 - 12x
= 3x(x - 4)
Possible expression for length = 3
Possible expression for breadth = x
Possible expression for height = (x - 4)
(ii) Volume : 12ky2 + 8ky - 20k
Since, volume is product of length, breadth and height therefore by factorizing the given volume, we can know the length, breadth and height of the cuboid.
12ky2 + 8ky - 20k
= 4k(3y2 + 2y - 5)
= 4k(3y2 +5y - 3y - 5)
= 4k[y(3y +5) - 1(3y + 5)]
= 4k (3y +5) (y - 1)
Possible expression for length = 4k
Possible expression for breadth = (3y +5)
Possible expression for height = (y - 1)
No comments:
Post a Comment